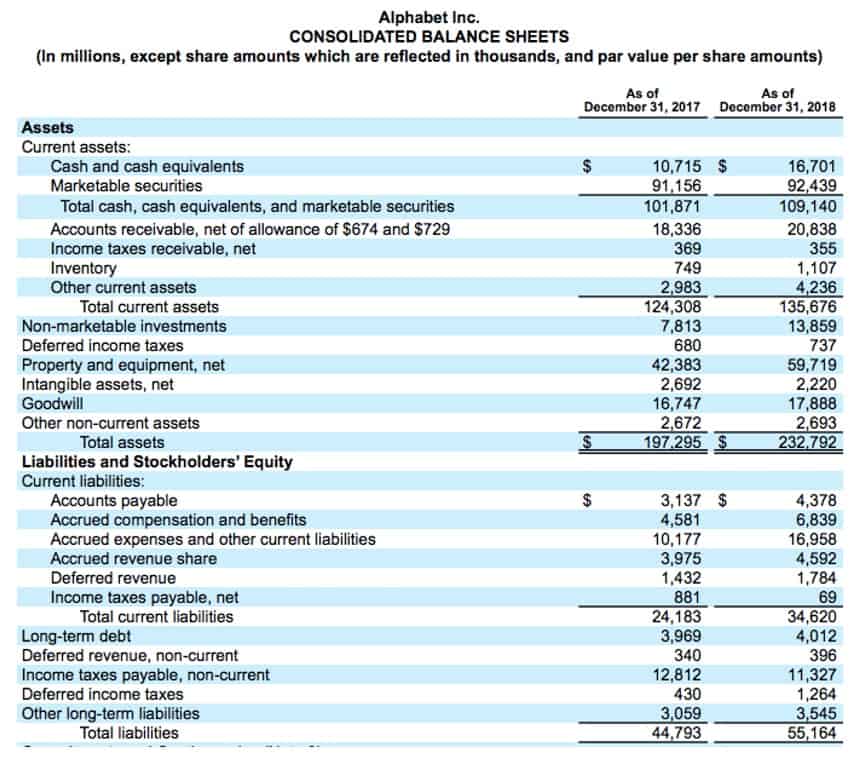
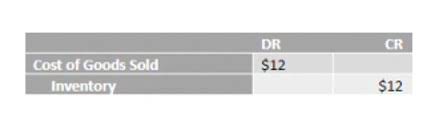
By following these steps, activity-based costing provides businesses with a clearer understanding of their cost structure and helps optimize resource use, leading to better financial performance and strategic decision-making. Once the activities are identified, they are grouped into cost pools, which are categories that group similar activities. For example, activities like machine maintenance, quality control and assembly might all fall under a production cost pool. Grouping activities into cost pools helps simplify the allocation process and makes it easier to assign costs systematically. ProjectManager helps with activity-based costing with robust Gantt charts that allow project managers to track, manage and assign costs to specific activities within a project. Use it to create tasks and subtasks for projects, which can then be linked to specific activities that will incur costs.
- Target costing focuses on designing products that meet customer needs and are profitable.
- Activity-based costing provides a more precise method for allocating overhead costs by linking expenses to specific activities.
- Design engineers are instrumental in the initial stages of target costing, where they collaborate with marketing and finance teams to set a competitive market price for the product.
- It is, thus, the difference between estimated selling price of a proposed product with specified functionality and quality and the target margin.
- Many firms have turned to target costing as a way of improving the price and quality of theirproducts, creating a benefit in terms of a company’s profits as well as increased customer satisfaction.
- Target costing decomposes the target cost from product level to component level.
A fair degree of judgement is needed where the allowable cost and the target cost differ. The company estimates that if it were to spend an additional £15,000 on design, manufacturing costs/unit could be reduced. Target Pricing ensures market competitiveness by aligning product features and pricing with consumer value perceptions, thereby strategically positioning the product in the market.
- For every problem area outlined above the proper solution is retaining strong control over the design team, which calls for a good team leader.
- In short, in target costing, the cost of product is first estimated and then designed the product to meet that cost.
- This design activity includes specifying the raw materials and components to be used as well as the labour, machinery, and other elements of the production process.
- Target costing is particularly useful in industries that have low profit margins and high competition.
This free workload analyst template for Excel helps keep team members from being overallocated or underutilized, which prevents burnout and keeps projects on budget. To better understand how the ABC technique works, let’s look at a real-life scenario about a furniture company that manufactures different chairs. Target cost allows for a simulation of the organization’s future and forces to reflect from upstream processes, according to their future implications.
Group Activities into Cost Pools
In target costing, companies leverage their ability to monitor and control their cost to generate a profit. In target costing process, the cost which is directly influenced by it is given priority, which includes material and purchase parts, tooling cost, conversion cost, development expenses and depreciation. Nevertheless, it is a comprehensive cost management technique, so all those cost and assets which are influenced by initial product planning decision are taken into account. Target Cost refers to an estimate of product cost reached by deducting a desired profit margin from the competitive market price.
What are the key steps in implementing target costing in procurement?
This price serves as the basis for determining the allowable costs for manufacturing and other expenses. The target price is the price point at which the product must be sold to remain competitive in the market. This method ensures that the product is priced competitively while guiding the development team to meet this price without sacrificing essential features or quality. Apple’s strategic use of target costing for the iPhone involved close collaboration with suppliers to innovate and reduce component costs.
Activity based costing is only one way to control costs in project management. They lead to some of our more recent pieces on job costing, cost control techniques and more. Assign the calculated activity rates to specific products or services based on their usage of the identified cost drivers. A cost driver is a factor that directly influences the cost of an activity. For example, the number of machine hours might be the cost driver for machine maintenance, or the number of customer orders might be the cost driver for order processing.
How ProjectManager Helps With Activity-Based Costing
After determining the overall target cost, cost targets for each of the components, subsystems and elements that go into making up the set of total costs to be included are found out. A matrix is created which target costing and how to use it relates different product features to the various elements making up the product. The target price is determined on the basis of market factors, e.g., company’s status in the market, marketing strategy, competitive price structure, anticipated market share as per demand forecasting etc. The crux of the entire matter is that target cost is the dependent variable. To repeat, market-based price is determined in the first place followed by desired profitability and target cost is simply arrived at by deducting profit from the price.
Life Cycle Costing
Cost-engineering techniques are applied in the process of cost reduction. Just-in-time approach, total quality control, value analysis also termed as value engineering etc. are some of the important methods used. Target cost is the difference between target sales minus target margin.
By identifying and eliminating unnecessary costs, simplifying designs, and streamlining production processes, they managed to lower overall costs. This comprehensive approach enabled the company to offer competitively priced products. The successful implementation of target costing contributed to a notable increase in market share and profitability. The first step is to review the marketplace in which the company wants to sell products. The design team needs to determine the set of product features that customers are most likely to buy, and the amount they will pay for those features.
If the product designed cannot be produced in the cost range decided, value engineering is used to drive down the product cost to a level, at which target price and margin can be attained. In both the conventional approaches, the focus is on cost reduction and not on cost management. Both the approaches induce production efficiencies to apply after the product design stage. If the profit margin is below an acceptable level, the product is redesigned, if possible, to reduce the cost until the desired profit margin is achieved. The approach is to design a product so that it can be produced at the lowest cost, and then a desired margin is added to the estimated cost to determine the selling price of the new product. The target costing approach is radically different from the conventional approach for price fixation and cost management.
The design team uses one of the approaches noted below to more tightly focus its cost reduction efforts. The method involves several functions in a unique approach to market research, applying methods for product design, management control for revaluating items and purchases for choosing purchased and delivered components. Hence, the sales department must ascertain what value the product has for the customers as compared to competitive products available in the market. It will help in advising the management in fixing the selling price of the product. Current estimated costs must be compared with the target costs – the comparison should be on a continuous basis and at each and every stage of production.
The development of the process can be lengthened to a considerable extent since the design team may require a number of design iterations before it can devise low cost product that meets the target cost and margin criteria. This occurrence is most common when the project manager is unwilling to discontinue a design project that cannot meet its costing goals within a reasonable time frame. Talk with customers about a new product concept, find out which features they like and don’t like, and find out how much they would pay. Subtract an acceptable profit margin, and you’re left with the target cost of the product.
This method provides a detailed understanding of what a product should cost to produce, enabling procurement teams to identify potential savings and negotiate more effectively with suppliers. By examining each cost element, such as raw materials, labor, and overhead, procurement professionals can develop a comprehensive cost model that serves as a benchmark for negotiations. With target costing, the company will try to reduce nonvalue features from the products as they will not impair the product’s quality. Those features only incur the cost for the company without providing value to customers.